4. Add firewall
4.1. Ufw
Section titled “4.1. Ufw”Installing and Configuring UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) UFW is a user-friendly interface for managing firewall rules in Linux.
- Check Current Status:
sudo ufw statusEnsures that UFW is installed and shows whether it’s active or not. In this case, the status is “Inactive,” meaning the firewall is not yet enabled.
Set Default Rules:
sudo ufw default deny incomingsudo ufw default allow outgoingThese commands define baseline rules:
- Deny incoming traffic: Blocks all incoming connections unless explicitly allowed.
- Allow outgoing traffic: Permits all outgoing requests from the server.
Allow Incoming Traffic on Specific Ports: These commands open ports required for essential services:
sudo ufw allow sshsudo ufw allow httpsudo ufw allow https/tcpsudo ufw allow https/udp- Port 22 (SSH): Needed for remote management.
- Port 80 (HTTP): Allows visitors to access web pages over HTTP.
- Ports 443 (HTTPS TCP/UDP): Enables secure communication over HTTPS. Opening only specific ports reduces the server’s attack surface.
Enable the Firewall:
sudo ufw enableActivates UFW to enforce the configured firewall rules.
- Recheck Status:
sudo ufw statusDisplays active rules applied by UFW. For example:
Status: active
To Action From-- ------ ----22/tcp ALLOW Anywhere80/tcp ALLOW Anywhere443/tcp ALLOW Anywhere443/udp ALLOW Anywhere22/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)80/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)443/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)443/udp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)The listed ports and their protocols (e.g., TCP/UDP) confirm the rules are in place. IPv6 rules are included if the server supports it.
4.2. Provider-Specific Firewall
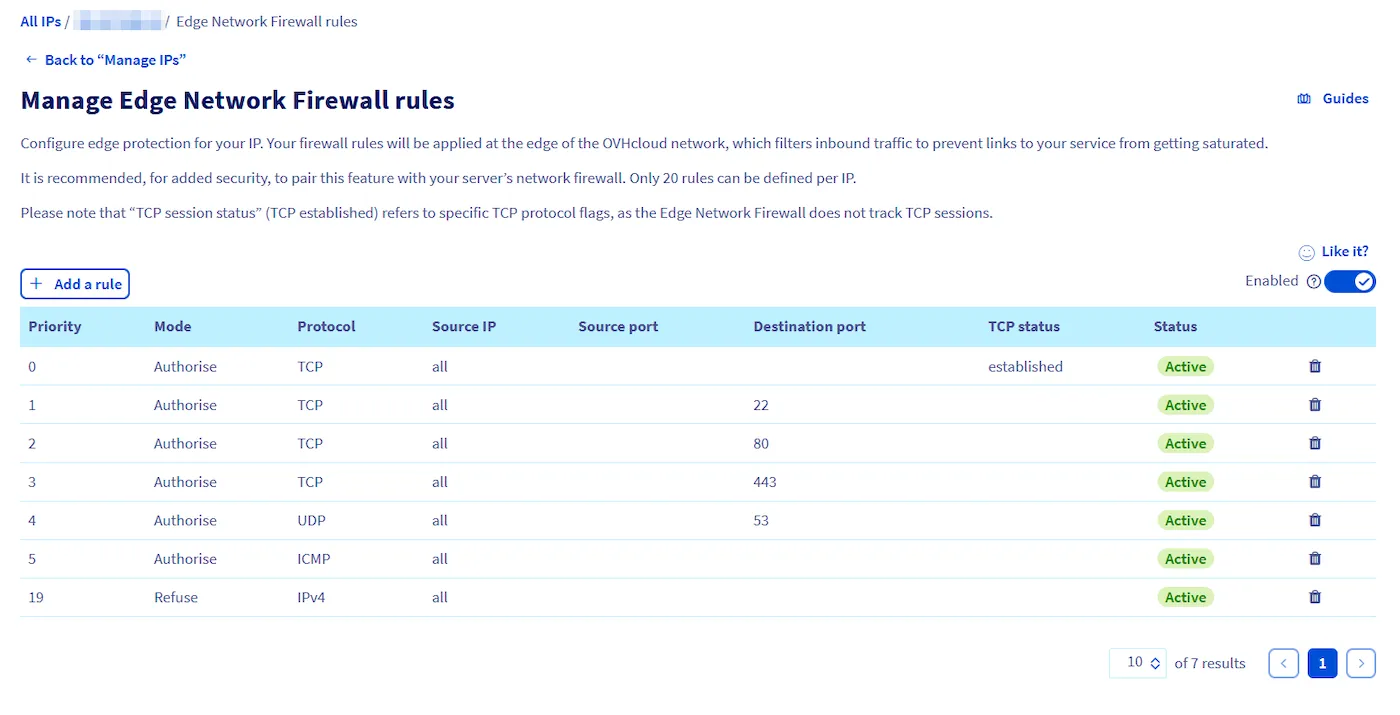
Section titled “4.2. Provider-Specific Firewall”Many cloud or dedicated server providers, such as OVHCloud, offer built-in firewalls. These firewalls add an additional layer of protection by filtering traffic before it reaches your server.
Follow instruction at : https://help.ovhcloud.com/csm/fr-dedicated-servers-firewall-network?id=kb_article_view&sysparm_article=KB0043455
- Configuring Firewall Rules: Following the OVHCloud example:
- Keep ports for essential services open:
- SSH (22): For remote server management.
- HTTP (80) & HTTPS (443): For web traffic.
- UDP (53): Common for DNS communication.
- Allow ICMP: Useful for diagnostics (e.g., ping).
- Ensure only required ports are open to minimize vulnerability.
- Provider-level firewalls are highly effective since they block unwanted traffic at the network level (before it reaches your server).
4.2.1 Example configuration
Section titled “4.2.1 Example configuration”To ensure that only the SSH (22), HTTP (80), HTTPS (443), and UDP (53) ports remain open when allowing ICMP, follow the rules below: